Ne Cation Or Anion
Main Difference
- Anion Names and Formulas Metallic atoms hold some of their electrons relatively loosely, and as a result, they tend to lose electrons and form cations. In contrast, nonmetallic atoms attract electrons more strongly than metallic atoms, and so nonmetals tend to gain electrons and form anions.
- It should be noted that the number of neutrons is not important while determining whether an atom or a molecule is an anion or not. Similar to the cations, anions are also symbolized by the number denoting its charge preceding a minus sign. For instance, the symbol of chlorine Cl – carries a single negative charge.
- Ionic radius, r ion, is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, they are sometimes treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation and anion gives the distance between the ions in a crystal lattice.Ionic radii are typically given in units of either picometers (pm).
The main difference between Atom and Ion is that Atom is the fundamental unit of matter. It contains the equal number of electrons and protons in their nucleus, thus bear a net neutral electrical charge, whereas Ion is an atom that contains the unequal number of protons and electrons in it and therefore carries a net positive or negative charge.
Atom vs. Ion
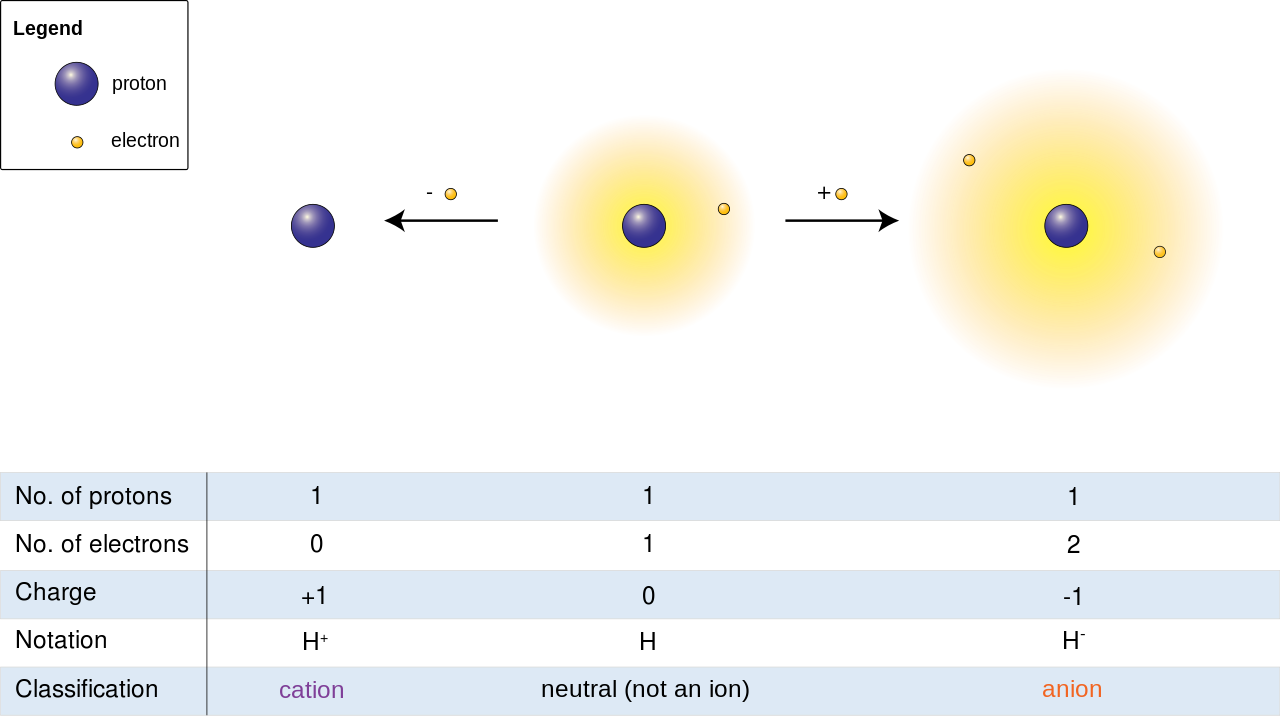
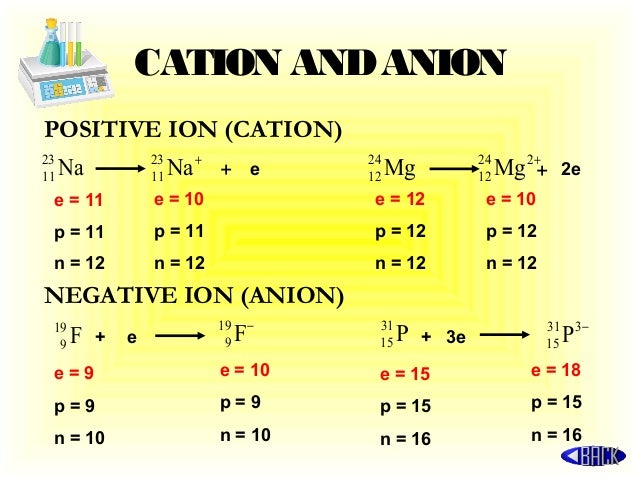
Cation Formation. Cations are the positive ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons. The most commonly formed cations of the representative elements are those that involve the loss of all of the valence electrons. Consider the alkali metal sodium (Na).
An atom is a fundamental unit of all matters in this universe, thus deriving all components. In contrast, Ion is charge bearing atom, i.e. that contains a positive or a negative charge. Atoms have no further classifications and is a fundamental unit they compose of matter founded in the universe, but, Ions further classified into two types as Cations and Anions based on their carrying a positive or negative charge.
Atoms are composed of equal protons and electrons as in their existing natural forms as a whole with varying numbers of electrons and protons with varying atomic numbers. Whereas, Ions contain an odd or unequal number of electrons and protons as atom attracts an electron in their outermost shell or lose an electron to another atom to become an ion.
Is Ne A Cation Or Anion
Atoms bear a net neutral charge due to the equal number of protons that carry a positive charge and electrons that carry a negative charge. While Ions bear a net positive or a negative charge due to the unequal number of electrons and protons, i.e. they attract an electron in their outermost shell or lose an electron to another atom. Atoms do not bear any electrical charge, i.e. net neutral charge thus does not show any attraction or repulsion to electric fields. However, as Ions carry a net positive or a negative charge; therefore, they are attractive or repulsive to electric fields as per their bearing charge.
Atoms denoted by a simple molecular formula of an element are represented neutral due to no charge. In contrast, Ions are denoted by a charge either negative or positive, representing the number of excess or lost electrons as per their carrying charge. Atoms have examples as Neon is represented by Ne and Iron is represented by Fe and respectively, whereas, Ions have examples as Cobalt ion is denoted by Co 2+ and Nitride – N3- and respectively.
Comparison Chart
| Atom | Ion |
| The fundamental unit of matter in this universe contains an equal number of electrons and protons. | Atoms that either contains a negative or a positive charge. |
| Classifications | |
| No further Classification | Classified into Cations and Anions |
| Number of Electrons | |
| Equal to the number of Protons | Not Equal to the number of Protons |
| Electrical Charge | |
| Neutral | Positive or Negatively charged |
| Reaction to Electric Field | |
| No reaction | Attracted or repulsed |
| Presentation | |
| Neutral Formula of Atom | The formula of Atom with respect to bearing charge |
| Examples | |
| Neon as Ne, Iron by Fe, etc. | Cobalt ion as Co 2+ and Nitride as N3- |
What is an Atom?
Atoms are the fundamental unit of all matters in this universe as they derive all components. In early times, scientists believed that Atoms could not further divide, which was voided by the discovery of protons, electron, and nucleus. The atomic theory describes the structure of an Atom as how an Atom is composed of electrons and protons. In modern times, this theory is preceded by modern atomic theory according to which Atoms composed of two components. These components are the nucleus and subatomic particles.
Atoms have no further classifications and being a fundamental unit they compose of matter founded in the universe. And as described above, composed of equal protons and electrons as in their existing natural forms with varying atomic number. Atoms bear as a result net neutral charge due to the equivalent number of protons that carry a positive charge and electrons that carry a negative charge. They also do not show any attraction or repulsion to electric fields.
Atoms can form chemical bonds with each other to form molecules and compounds. These bonds can either be a covalent bond, ionic bond, or metallic bonds. These bonds are formed between the Atoms due to the exchange of electrons with each other.
However, protons and neutrons do not directly take part in bond formation. Atoms denoted by a simple molecular formula of an element and are represented neutral due to no charge. Some common examples of Atoms include Neon Atoms, which are represented by Ne and Hydrogen, which is represented by H and, respectively.
What is Ion?
Ion is an Atom or Molecules that bear a net charge, i.e. that contain a positive or a negative charge. Because when an Atom or a Molecule attracts an electron in their outermost shell or loses an electron to another Atom, it becomes an Ion. They further classified into two types as Cations and Anions based on their carrying a positive or negative charge.
Anions are the Ions that bear a net negative charge by gaining excess electrons from their surrounding atoms or molecules because the protons in the nucleus get unable to neutralize the impact of gained electrons. Cations are the kind of atoms or molecules that, by losing electrons from their outermost shell exposed to the environment, bear a net positive charge.
Ions as bear a net positive or a negative charge, thus show attraction or repulsion towards electric fields as per their bearing charge. They are also able to form ionic bonds. These ionic bonds are formed in response to these attracted ions, which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force of attraction because of two opposite charges on these atoms. These Ions are denoted by a charge, either negative or positive, representing the number of excess or lost electrons. Common examples of Ions are, Cobalt that is denoted by Co 2+, and Nitride that is denoted by N3- and respectively.
Key Differences
- An atom is a fundamental unit of all matters in this universe; on the contrary, Ions are positive or negative charge bearing atoms.
- Atoms are composed of equal protons and electrons as in their existing natural forms; on the flip side, Ions contain an unequal number of electrons and protons by attracting or losing an electron in their outermost shell.
- Atoms bear a net neutral charge due to an equal number of protons and electrons, on the other hand, Ions bear a net positive or a negative charge due to an unequal number of electrons and protons.
- Atoms do not show any attraction or repulsion to an electric field, whereas, as Ions bear a net positive or a negative charge, they show attraction or repulsion to electric fields as per their bearing charge.
- Atoms are denoted by a neutral molecular formula of an element due to no charge. On the contrary, Ions are denoted by a charge either negative or positive as per the number of electrons with respect to protons.
- Atoms have no further classifications, on the flip side, Ions further classified into two types as Cations and Anions based on their carrying a positive or negative charge.
- Atoms have examples as the Hydrogen atom represented by H and Iron is represented by Fe, whereas the example of Ions is; Cobalt, which is denoted by Co 2+ and Nitride, which is denoted by N3-.
Conclusion
Atoms are the fundamental unit of matter that contains an equal number of electrons and protons and bears a net neutral electrical charge. However, Ions composed of atoms that bear a net positive or negative charge due to an unequal number of protons and electrons.
Be Cation Or Anion
Department of Chemistry and Physics |
| Cation/ Anion List |
Students enrolled in Dr. Draganjac's Introduction to Chemistry (CHEM1003), General Chemistry I (CHEM1013) and General Chemistry II (CHEM1023) classes are responsible for learning the names and formulae for the common acids and common reagents and for learning the names, formulae and the charges for the common cations and anions listed below:
| Name | Formula | Other name(s) |
| Aluminum | Al+3 | |
| Ammonium | NH4+ | |
| Barium | Ba+2 | |
| Calcium | Ca+2 | |
| Chromium(II) | Cr+2 | Chromous |
| Chromium(III) | Cr+3 | Chromic |
| Copper(I) | Cu+ | Cuprous |
| Copper(II) | Cu+2 | Cupric |
| Iron(II) | Fe+2 | Ferrous |
| Iron(III) | Fe+3 | Ferric |
| Hydrogen | H+ | |
| Hydronium | H3O+ | |
| Lead(II) | Pb+2 | |
| Lithium | Li+ | |
| Magnesium | Mg+2 | |
| Manganese(II) | Mn+2 | Manganous |
| Manganese(III) | Mn+3 | Manganic |
| Mercury(I) | Hg2+2 | Mercurous |
| Mercury(II) | Hg+2 | Mercuric |
| Nitronium | NO2+ | |
| Potassium | K+ | |
| Silver | Ag+ | |
| Sodium | Na+ | |
| Strontium | Sr+2 | |
| Tin(II) | Sn+2 | Stannous |
| Tin(IV) | Sn+4 | Stannic |
| Zinc | Zn+2 |
Common Anions: (ions grouped by charge)
 (anions grouped by periodic position)
(anions grouped by periodic position)| Simple ions: | |||
| Hydride | H- | Oxide | O2- |
| Fluoride | F- | Sulfide | S2- |
| Chloride | Cl- | Nitride | N3- |
| Bromide | Br- | ||
| Iodide | I- | ||
| Oxoanions: | |||
| Arsenate | AsO43- | Phosphate | PO43- |
| Arsenite | AsO33- | Hydrogen phosphate | HPO42- |
| Dihydrogen phosphate | H2PO4- | ||
| Sulfate | SO42- | Nitrate | NO3- |
| Hydrogen sulfate | HSO4- | Nitrite | NO2- |
| Thiosulfate | S2O32- | ||
| Sulfite | SO32- | ||
| Perchlorate | ClO4- | Iodate | IO3- |
| Chlorate | ClO3- | Bromate | BrO3- |
| Chlorite | ClO2- | ||
| Hypochlorite | OCl- | Hypobromite | OBr- |
| Carbonate | CO32- | Chromate | CrO42- |
| Hydrogen carbonate or Bicarbonate | HCO3- | Dichromate | Cr2O72- |
| Anions from Organic Acids: | |||
| Acetate | CH3COO- | formate | HCOO- |
| Others: | |||
| Cyanide | CN- | Amide | NH2- |
| Cyanate | OCN- | Peroxide | O22- |
| Thiocyanate | SCN- | Oxalate | C2O42- |
| Hydroxide | OH- | Permanganate | MnO4- |